Array And Slice The Rust And Golang Style
Array and Slice is the basic element of a program in modern high-order programming language, but how different language deal with them? We will inspect the Golang and Rust way.
1. Array, the same kind of things in a sequence
Array have the following attribute:
- the size is know in compile time
- the type of all elements are the same
- you can not change the elements by default[Rust]
a := [3]int{1, 2, 3}
fmt.Println(a)
a[1] = 4
fmt.Println(a)
running result:

the array in golang can be changed.
let rs_arr = [1,2,3];
println!("{:?}", rs_arr);
rs_arr[2] = 4;
println!("{:?}", rs_arr);
running result:

the default(no mutable) array in rust can’t be changed in runtime.
2. Slice, the mask on an array
slice is more like a data struct, which contains:
- a pointer to the underline array element
- length of the slice
- capacity of the slice
type IntSlice struct
{
ptr *int
len, cap int
}
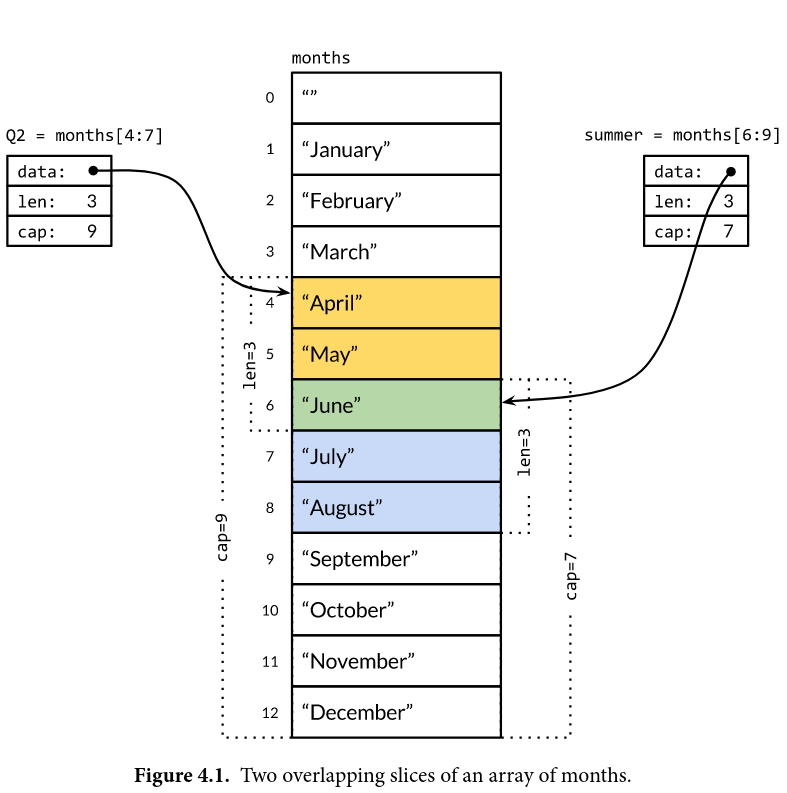
the follwing is two slices have the same underlying array:
A simple program in golang, delete adjecent duplicate word in a string:
func RemoveAdjacentDuplicateString(s []string) []string {
dupnum := 0
curpos := 1
//dup adj never can happen
if len(s) <= 1 {
return s
}
for curpos < len(s)-dupnum {
if s[curpos] == s[curpos-1] {
copy(s[curpos-1:], s[curpos:])
dupnum++
} else {
curpos++
}
}
return s[:len(s)-dupnum]
}
3. Slice, the rust style
The following a code sneppet from “The Rust Programming Language”.
fn first_word(s: &String) -> &str {
let bytes = s.as_bytes();
for (i, &item) in bytes.iter().enumerate() {
if item == b' ' {
return &s[0..i];
}
}
&s[..]
}
&s[0..i] is a slice reference to string.
4. Summary
Slice is more generally used than array, use it! :)